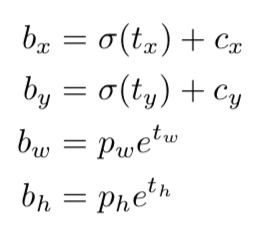Pytorch实现You Only Look Once - V3(下简称yolo) yolo是一种使用深度卷积神经网络学得的特征来检测对象的目标检测器
首先来看下yolo网络结构
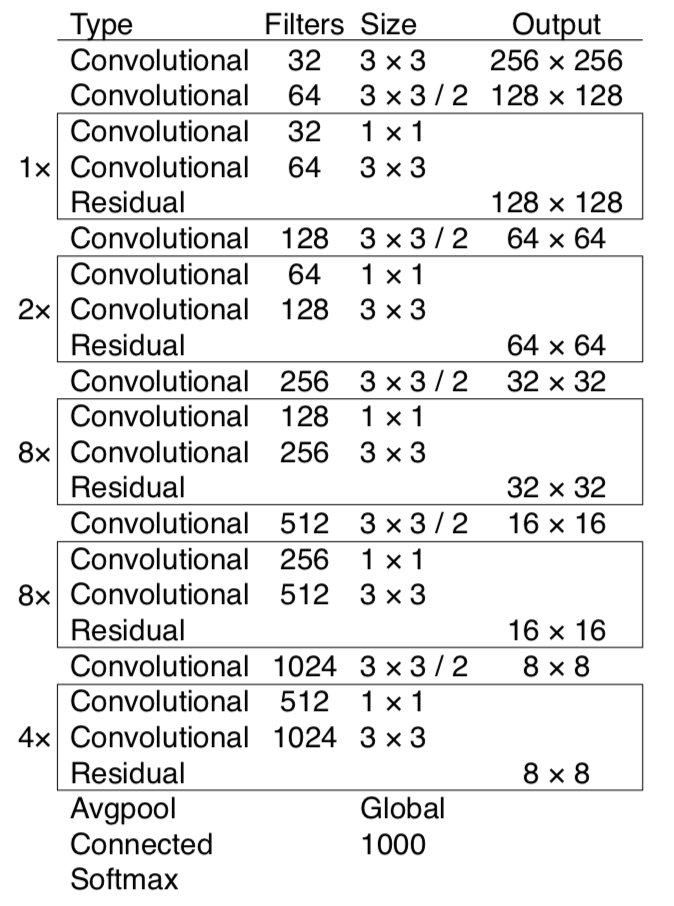
使用: 卷积层(不带bias)+BatchNorm2d+LeakyReLU,Residual,单独卷积层(带bias), 没有使用: Pooling
在yolo中,使用的改进后的darknet,去掉全连接层,加入Route,上采样,并提取中间特征进行组合
代码:
卷积层(不带bias)+BatchNorm+LeakyReLU
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ind, outd, kr_size, stride, padding, lr=0.1, bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ind, outd, kr_size, stride, padding, bias=bias),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outd),
nn.LeakyReLU(lr, inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layers(x)
网络中间循环层:1、2、8、8、4
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, conv_1, conv_2, times):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for _ in range(times):
self.layers.append(BasicConv(*conv_1))
self.layers.append(BasicConv(*conv_2))
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
for index, layer in enumerate(self.layers):
x = layer(x)
if index % 2 == 1:
x += residual
residual = x
return x
预测层
class BasicPred(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
structs,
use_cuda,
anchors,
classes=80,
height=416,
route_index=0):
super().__init__()
self.ri = route_index
self.classes = classes
self.height = height
self.anchors = anchors
self.torch = torch.cuda if use_cuda else torch
in_dim = structs[0]
self.layers = nn.ModuleList()
for s in structs[1:]:
if len(s) == 4:
out_dim, kr_size, stride, padding = s
layer = BasicConv(in_dim, out_dim, kr_size, stride, padding)
else:
out_dim, kr_size, stride, padding, _ = s
layer = nn.Conv2d(in_dim, out_dim, kr_size, stride, padding)
in_dim = out_dim
self.layers.append(layer)
def forward(self, x):
for index, layer in enumerate(self.layers):
x = layer(x)
if self.ri != 0 and index == self.ri:
output = x
detections = self.predict_transform(x.data)
if self.ri != 0:
return detections, output
else:
return detections
5组循环层
class LayerOne(BasicLayer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__((64, 32, 1, 1, 0),
(32, 64, 3, 1, 1), 1)
class LayerTwo(BasicLayer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__((128, 64, 1, 1, 0),
(64, 128, 3, 1, 1), 2)
class LayerThree(BasicLayer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__((256, 128, 1, 1, 0),
(128, 256, 3, 1, 1), 8)
class LayerFour(BasicLayer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__((512, 256, 1, 1, 0),
(256, 512, 3, 1, 1), 8)
class LayerFive(BasicLayer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__((1024, 512, 1, 1, 0),
(512, 1024, 3, 1, 1), 4)
预测层结构和实现
DETECT_DICT = {
'first': [1024, (512, 1, 1, 0), (1024, 3, 1, 1), (512, 1, 1, 0), (1024, 3, 1, 1), (512, 1, 1, 0), (1024, 3, 1, 1), (255, 1, 1, 0, 0)],
'second': [768, (256, 1, 1, 0), (512, 3, 1, 1), (256, 1, 1, 0), (512, 3, 1, 1), (256, 1, 1, 0), (512, 3, 1, 1), (255, 1, 1, 0, 0)],
'third': [384, (128, 1, 1, 0), (256, 3, 1, 1), (128, 1, 1, 0), (256, 3, 1, 1), (128, 1, 1, 0), (256, 3, 1, 1), (255, 1, 1, 0, 0)],
}
class FirstPred(BasicPred):
def __init__(self,
structs,
use_cuda,
route_index=4,
anchors=[(116, 90), (156, 198), (373, 326)]):
super().__init__(structs, use_cuda, anchors, route_index=route_index)
class SecondPred(BasicPred):
def __init__(self,
structs,
use_cuda,
route_index=4,
anchors=[(30, 61), (62, 45), (59, 119)]):
super().__init__(structs, use_cuda, anchors, route_index=route_index)
class ThirdPred(BasicPred):
def __init__(self,
structs,
use_cuda,
classes=80,
height=416,
anchors=[(10, 13), (16, 30), (33, 23)]):
super().__init__(structs, use_cuda, anchors)
整个网络结构实现,可以结合darknet图阅读代码
class DarkNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, use_cuda):
super().__init__()
self.conv_1 = BasicConv(256, 512, 3, 2, 1)
self.seq_1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(3, 32, 3, 1, 1),
BasicConv(32, 64, 3, 2, 1),
LayerOne(),
BasicConv(64, 128, 3, 2, 1),
LayerTwo(),
BasicConv(128, 256, 3, 2, 1),
LayerThree(),
)
self.seq_2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(512, 1024, 3, 2, 1),
LayerFive(),
FirstPred(DETECT_DICT["first"], use_cuda)
)
self.layer_4 = LayerFour()
self.uns_1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(512, 256, 1, 1, 0),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="bilinear")
)
self.uns_2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(256, 128, 1, 1, 0),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="bilinear")
)
self.pred_2 = SecondPred(DETECT_DICT["second"], use_cuda)
self.pred_3 = ThirdPred(DETECT_DICT["third"], use_cuda)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.seq_1(x)
r_0 = x
x = self.layer_4(self.conv_1(x))
r_1 = x
det_1, x = self.seq_2(x)
x = self.uns_1(x)
x = torch.cat((x, r_1), 1)
det_2, x = self.pred_2(x)
x = self.uns_2(x)
x = torch.cat((x, r_0), 1)
det_3 = self.pred_3(x)
return torch.cat((det_1, det_2, det_3), 1)
网络结构介绍完毕,接下来介绍不同维度特征映射到同一空间和物体预测的原理
网络会在预测1、2、3分别输出特征,结构分别是(假设图片裁剪为416X416): [b, 255, 13, 13], [b, 255, 26, 26], [b, 255, 52, 52], 其中b为batch-size
注:按论文中给出,针对coco数据集的锚点 (10×13), (16×30), (33×23), (30×61), (62×45), (59× 119), (116 × 90), (156 × 198), (373 × 326)
- 将特征转换为 [b, 13X13X锚点数, 5+分类数], [b, 26X26X锚点数, 5+分类数] , [b, 52X52X锚点数, 5+分类数]
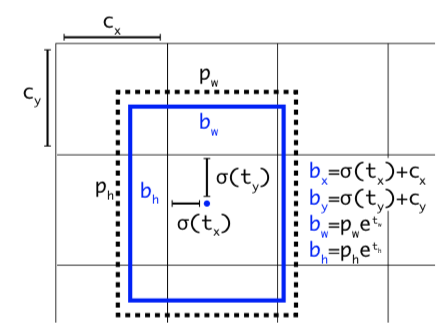
- 对x和y进行sigmoid,并加上对应的offset(下图Cx, Cy)
- 对h和w进行exp,并乘以对应的锚点值
- 对x,y,h,w乘以对应的步幅,即:416/13, 416/26, 416/52
- 最后,使用sigmoid对Objectness和Classes confidence进行sigmoid得到0~1的概率,之所以用sigmoid取代之前版本的softmax,原因是softmax会扩大最大类别概率值而抑制其他类别概率值
def predict_transform(self, prediction):
""" borrowed from https://github.com/ayooshkathuria/YOLO_v3_tutorial_from_scratch/blob/master/util.py#L47
"""
batch_size = prediction.size(0)
stride = self.height // prediction.size(2)
grid_size = self.height // stride
bbox_attrs = 5 + self.classes
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
prediction = prediction.view(
batch_size, bbox_attrs * num_anchors, grid_size * grid_size)
prediction = prediction.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
prediction = prediction.view(
batch_size, grid_size * grid_size * num_anchors, bbox_attrs)
anchors = [(a[0] / stride, a[1] / stride) for a in self.anchors]
prediction[:, :, 0] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:, :, 0])
prediction[:, :, 1] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:, :, 1])
grid = np.arange(grid_size)
a, b = np.meshgrid(grid, grid)
x_offset = self.torch.FloatTensor(a).view(-1, 1)
y_offset = self.torch.FloatTensor(b).view(-1, 1)
x_y_offset = torch.cat((x_offset, y_offset), 1).repeat(
1, num_anchors).view(-1, 2).unsqueeze(0)
prediction[:, :, :2] += x_y_offset
anchors = self.torch.FloatTensor(anchors)
anchors = anchors.repeat(grid_size * grid_size, 1).unsqueeze(0)
prediction[:, :, 2:4] = torch.exp(prediction[:, :, 2:4]) * anchors
prediction[:, :, :4] *= stride
# sigmoid Objectness and classes confidence
prediction[:, :, 4:] = torch.sigmoid(prediction[:, :, 4:])
return prediction
预测
- 将x,y,h,w -> 对角坐标, 这样可以方便后面计算iou和构图。
- 过滤掉Objectness小于confidence(论文中给的0.5)向量
- 筛选出所有类别中最大分数和index,对同一类别的的向量计算iou,过滤掉大于阈值的向量
iou原理:(图a 交 图b) / (图a 并 图b)
def iou(box1, box2):
x1, y1 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1]
b1_w, b1_h = box1[:, 2] - x1 + .1, box1[:, 3] - y1 + .1
x2, y2, = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1]
b2_w, b2_h = box2[:, 2] - x2 + .1, box2[:, 3] - y2 + .1
end_x = torch.min(x1 + b1_w, x2 + b2_w)
start_x = torch.max(x1, x2)
end_y = torch.min(y1 + b1_h, y2 + b2_h)
start_y = torch.max(y1, y2)
a = (end_x - start_x) * (end_y - start_y)
return a / (b1_w * b1_h + b2_w * b2_h - a)
预测代码
def predict(self, prediction, nms_conf=0.4):
"""
prediction:
0:3 - x, y, h, w
4 - confidence
5: - class score
"""
def iou(box1, box2):
x1, y1 = box1[:, 0], box1[:, 1]
b1_w, b1_h = box1[:, 2] - x1 + .1, box1[:, 3] - y1 + .1
x2, y2, = box2[:, 0], box2[:, 1]
b2_w, b2_h = box2[:, 2] - x2 + .1, box2[:, 3] - y2 + .1
end_x = torch.min(x1 + b1_w, x2 + b2_w)
start_x = torch.max(x1, x2)
end_y = torch.min(y1 + b1_h, y2 + b2_h)
start_y = torch.max(y1, y2)
a = (end_x - start_x) * (end_y - start_y)
return a / (b1_w * b1_h + b2_w * b2_h - a)
conf_mask = (prediction[:, :, 4] >
self.confidence).float().unsqueeze(2)
prediction = prediction * conf_mask
box_corner = prediction.new(*prediction.size())
box_corner[:, :, 0] = (prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2)
box_corner[:, :, 1] = (prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2)
box_corner[:, :, 2] = (prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2)
box_corner[:, :, 3] = (prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2)
prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4]
outputs = []
for index in range(prediction.size(0)):
image_pred = prediction[index] # [10647, 85]
max_score, max_index = torch.max(
image_pred[:, 5:], 1, keepdim=True)
image_pred = torch.cat(
(image_pred[:, :5], max_score, max_index.float()), 1) # [10647, 7]
non_zero_ind = (torch.nonzero(image_pred[:, 4])).view(-1)
if non_zero_ind.size(0) == 0:
continue
image_pred_ = image_pred[non_zero_ind, :]
img_classes = torch.unique(image_pred_[:, -1])
objects, img_preds = [], []
name = self.this_img_names[index].split("/")[-1]
for c in img_classes:
c_mask = image_pred_ * \
(image_pred_[:, -1] == c).float().unsqueeze(1)
class_mask_ind = torch.nonzero(c_mask[:, -2]).squeeze()
image_pred_class = image_pred_[class_mask_ind].view(-1, 7)
_, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(
image_pred_class[:, 4], descending=True)
image_pred_class = image_pred_class[conf_sort_index]
for i in range(image_pred_class.size(0) - 1):
try:
ious = iou(image_pred_class[i].unsqueeze(
0), image_pred_class[i + 1:])
except IndexError:
break
iou_mask = (ious < nms_conf).float().unsqueeze(1)
image_pred_class[i + 1:] *= iou_mask
non_zero_ind = torch.nonzero(
image_pred_class[:, 4]).squeeze()
image_pred_class = image_pred_class[non_zero_ind].view(
-1, 7)
img_preds.append(image_pred_class)
objects += [self.classes[int(x[-1])] for x in image_pred_class]
outputs.append((name, objects))
img_preds = torch.cat(img_preds, dim=0)
if self.rebuild:
self.tensor2img(img_preds, index, name)
return outputs
绘图代码
def tensor2img(self, tensor, index, name):
imgs_dim = self.imgs_dim[index] / self.img_size
img = self.imgs[index]
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
tensor[:, :4] = tensor[:, :4].clamp_(0, self.img_size) * imgs_dim
for t in tensor:
s_x, s_y, e_x, e_y = list(map(int, t[:4]))
label = self.classes[int(t[-1])]
color = random.choice(self.colors)
draw.rectangle([s_x, s_y, e_x, e_y], outline=color)
draw.text([s_x, s_y], label, fill=color, font=self.font)
del draw
img.save(os.path.join(self.result, "res_{}".format(name)))
预测结果
参考文献